Wasm 二进制结构
使用一个示例的 add.wat :
(module (func (export "add") (param $a i32) (param $b i32) (result i32) (local.get $a) (local.get $b) i32.add ))执行以下命令,-v 可以展示详细的编译信息,这里我们主要看编译码。
❯ wat2wasm -v add.wat0000000: 0061 736d ; WASM_BINARY_MAGIC0000004: 0100 0000 ; WASM_BINARY_VERSION; section "Type" (1)0000008: 01 ; section code0000009: 00 ; section size (guess)000000a: 01 ; num types; func type 0000000b: 60 ; func000000c: 02 ; num params000000d: 7f ; i32000000e: 7f ; i32000000f: 01 ; num results0000010: 7f ; i320000009: 07 ; FIXUP section size; section "Function" (3)0000011: 03 ; section code0000012: 00 ; section size (guess)0000013: 01 ; num functions0000014: 00 ; function 0 signature index0000012: 02 ; FIXUP section size; section "Export" (7)0000015: 07 ; section code0000016: 00 ; section size (guess)0000017: 01 ; num exports0000018: 03 ; string length0000019: 6164 64 add ; export name000001c: 00 ; export kind000001d: 00 ; export func index0000016: 07 ; FIXUP section size; section "Code" (10)000001e: 0a ; section code000001f: 00 ; section size (guess)0000020: 01 ; num functions; function body 00000021: 00 ; func body size (guess)0000022: 00 ; local decl count0000023: 20 ; local.get0000024: 00 ; local index0000025: 20 ; local.get0000026: 01 ; local index0000027: 6a ; i32.add0000028: 0b ; end0000021: 07 ; FIXUP func body size000001f: 09 ; FIXUP section size首先第一部分是 magic number,代表 \0asm 和 wasm 标准的版本号。
0000000: 0061 736d ; WASM_BINARY_MAGIC0000004: 0100 0000 ; WASM_BINARY_VERSION后面紧跟着的就是不同的 section。根据https://www.w3.org/TR/wasm-core-1/,一个 wasm 文件可能会有以下这些 section:
| Id | Section | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | custom section | |
| 1 | type section | 包含函数签名的信息 |
| 2 | import section | 定义从其他模块导入的信息 |
| 3 | function section | 提供函数签名的引用信息 |
| 4 | table section | |
| 5 | memory section | 包含线性内存的信息 |
| 6 | global section | |
| 7 | export section | 定义导出到其他模块的信息 |
| 8 | start section | |
| 9 | element section | |
| 10 | code section | 包含每个函数的指令信息 |
| 11 | data section | 定义初始化时要放入内存的数据 |
Type Section
这里的 Type 指函数类型,也就是它的签名。
$$ \mathtt{typesec} ::= ft^* : \mathtt{section}_1(\mathtt{vec}(\mathtt{functype})) \Rightarrow ft^* $$
以上面这个例子中的 Type Section 为例:
; section "Type" (1)0000008: 01 ; section code0000009: 00 ; section size (guess)000000a: 01 ; num types; func type 0000000b: 60 ; func000000c: 02 ; num params000000d: 7f ; i32000000e: 7f ; i32000000f: 01 ; num results0000010: 7f ; i320000009: 07 ; FIXUP section size这里开头两个字节的 section code 和 section size 在每个 section 都会出现,其中 section size 并不是必须的,但如果有的话,它的值会是这个 section 除了前两个字节的字节数,可以用来跳过这个 section。
可以看到后面 functype 的容器类型是 vector,紧跟着的 num types 表示函数签名的数量,然后就是各个签名。
$$ \mathtt{functype} ::= \mathtt{0x60} \quad t_1^* : \mathtt{vec}(\mathtt{valtype}) \quad t_2^* : \mathtt{vec}(\mathtt{valtype}) \Rightarrow [t_1^] \to [t_2^] $$
每个签名以 0x60 开头,然后是参数数量、参数类型和返回值数量、返回值类型。
0000009: 07 ; FIXUP section size这里这行并不是标准中提及的,而是因为 wat2wasm 是一个单遍编译器,所以它不会先计算大小(size 为 0)而是在最后再计算大小,用计算出的大小替换原来的 0。
Code Section
这个 section 存储函数的指令信息。
$$ \mathtt{codesec} ::= code^* : \mathtt{section}_{10}(\mathtt{vec}(\mathtt{code})) \Rightarrow code^* \ \mathtt{code} ::= size:\mathtt{u32} \quad code:\mathtt{func} \Rightarrow code \quad (\text{if } size = ||\mathtt{func}||) \ \mathtt{func} ::= (t^)^ : \mathtt{vec}(\mathtt{locals}) \quad e:\mathtt{expr} \Rightarrow \mathrm{concat}((t^)^), e^* \quad (\text{if } |\mathrm{concat}((t^)^)| < 2^{32}) \ \mathtt{locals} ::= n:\mathtt{u32} \quad t:\mathtt{valtype} \Rightarrow t^n $$
; section "Code" (10)000001e: 0a ; section code000001f: 00 ; section size (guess)0000020: 01 ; num functions; function body 00000021: 00 ; func body size (guess)0000022: 00 ; local decl count0000023: 20 ; local.get0000024: 00 ; local index0000025: 20 ; local.get0000026: 01 ; local index0000027: 6a ; i32.add0000028: 0b ; end0000021: 07 ; FIXUP func body size000001f: 09 ; FIXUP section sizenum functions 表示功能的数量,并根据该数量对功能进行解码。其余部分包括每个函数的局部变量定义和指令信息,需要反复解码。func body size 表示函数体的字节数。local decl count 表示局部变量的数量。如果是 0 则不采取任何行动,但如果大于 1,随后的字节序列定义了局部变量的类型。
Function Section
将函数体 (Code Section) 与类型信息 (Type Section) 关联。
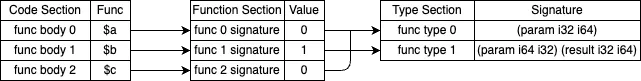
; section "Function" (3)0000011: 03 ; section code0000012: 00 ; section size (guess)0000013: 01 ; num functions0000014: 00 ; function 0 signature index0000012: 02 ; FIXUP section size开头是函数数量,然后跟着的是每个函数下标对应的类型下标。下面这张图中间就是 function section。
Memory Section
存储有关为 Runtime 提供线性内存的信息。内存可以以页为单位进行扩展,1 个页为 64KiB。内存格式为 (memory $initial $max) 。max 是可选项,如果未指定,则没有上限。
比如下面这个例子:
(module (memory 2 3))会被编译为
; section "Memory" (5)0000008: 05 ; section code0000009: 04 ; section size000000a: 01 ; num memories; memory 0000000b: 01 ; limits: flags000000c: 02 ; limits: initial000000d: 03 ; limits: maxnum memories 表示存储器的数量,但在规范的第 1 版中,每个模块只能定义一个存储器,因此该值实际上固定为 1。limits: flags 是一个值,用于确定 max 是否存在,也就是说,如果 0 只有 initial 存在;如果 1 则 initial 和 max 都存在。
Data Section
这个地方定义了内存的初始数据。
$$ \mathtt{datasec} ::= seg^* : \mathtt{section}_{11}(\mathtt{vec}(\mathtt{data})) \Rightarrow seg \ \mathtt{data} ::= x:\mathtt{memidx} \quad e:\mathtt{expr} \quad b^:\mathtt{vec}(\mathtt{byte}) \Rightarrow {\mathsf{data}~x, \mathsf{offset}~e, \mathsf{init}~b^} $$
数据格式为 (data $memory $offset $data) 并由以下要素组成:
$memory是放置数据的内存的索引$offset是计算内存偏移量以放置数据的指令序列$data是要存入内存的实际数据
比如下面这个例子:
(module (memory 1) (data 0 (i32.const 0) "Hello, World!\n"))对应的内存段:
; section "Data" (11)000000d: 0b ; section code000000e: 14 ; section size000000f: 01 ; num data segments; data segment header 00000010: 00 ; segment flags0000011: 41 ; i32.const0000012: 00 ; i32 literal0000013: 0b ; end0000014: 0e ; data segment size; data segment data 00000015: 4865 6c6c 6f2c 2057 6f72 6c64 210a ; data segment data数据被组织成称为 segments 的结构,可能有多个 segments。一个 segment 包括 header 和 data 两部分,其中 header 包含计算偏移和 data 保存实际数据。
data segment header 是保存元数据的区域,例如数据放置的内存和偏移量。每个 segment 都有一个 header.
segment flags 表示放置数据的内存的索引,在版本 1 固定为 0。
从 i32.const 至 end 是偏移量。data segment size 是实际放置数据的长度,而 data segment data 是要放入内存的实际数据。
Export Section
这里定义导出的存储器和函数。
$$ \mathtt{exportsec} ::= ex^* : \mathtt{section}_7(\mathtt{vec}(\mathtt{export})) \Rightarrow ex^* \ \mathtt{export} ::= nm:\mathtt{name} \quad d:\mathtt{exportdesc} \Rightarrow {\mathsf{name}~nm, \mathsf{desc}~d} \ \mathtt{exportdesc} ::= \mathtt{0x00} \quad x:\mathtt{funcidx} \Rightarrow \mathsf{func}~x \ \mid \mathtt{0x01} \quad x:\mathtt{tableidx} \Rightarrow \mathsf{table}~x \ \mid \mathtt{0x02} \quad x:\mathtt{memidx} \Rightarrow \mathsf{mem}~x \ \mid \mathtt{0x03} \quad x:\mathtt{globalidx} \Rightarrow \mathsf{global}~x $$
比如我们上面的例子:
; section "Export" (7)0000015: 07 ; section code0000016: 00 ; section size (guess)0000017: 01 ; num exports0000018: 03 ; string length0000019: 6164 64 add ; export name000001c: 00 ; export kind000001d: 00 ; export func index0000016: 07 ; FIXUP section size定义导出数量之后,每个导出的元素需要提供导出的名字、导出的类型和对应的下标。
Import Section
对应的也有导入模块外的元素的区域。
$$ \mathtt{import} ::= {\mathsf{module}~name, \mathsf{name}~name, \mathsf{desc}~importdesc} \ \mathtt{importdesc} ::= \mathsf{func}~typeidx \ \mid \mathsf{table}~tabletype \ \mid \mathsf{mem}~memtype \ \mid \mathsf{global}~globaltype $$
对于导入,和 export 对应,我们只需要额外知道一个模块名。导入格式为 (import $module $name $type) 。$module 是模块名称、$name 是要导入的函数或内存的名称,而 $type 包含类型定义信息。对于函数,它包含函数的签名信息;对于内存,它定义了 min 和 max 内存信息。
比如下面这个例子,从 adder 导入了一个 add 函数。
(module (import "adder" "add" (func (param i32 i32) (result i32))))对应:
; section "Type" (1)0000008: 01 ; section code0000009: 07 ; section size000000a: 01 ; num types; func type 0000000b: 60 ; func000000c: 02 ; num params000000d: 7f ; i32000000e: 7f ; i32000000f: 01 ; num results0000010: 7f ; i32; section "Import" (2)0000011: 02 ; section code0000012: 0d ; section size0000013: 01 ; num imports; import header 00000014: 05 ; string length0000015: 6164 6465 72 ; import module name (adder)000001a: 03 ; string length000001b: 6164 64 ; import field name (add)000001e: 00 ; import kind000001f: 00 ; import signature indexstring length 表示字符字节序列的长度、import module name 表示实际模块名称的字节序列,而 import field name 表示要导入的函数或存储器名称的字节序列。import kind 表示导入类型,其中 0 用于功能。import signature index 指向函数签名信息的索引,指向 func type 0 在 Type Section 。